A Hazardous Workplace
Healthcare workers are at higher risk for workplace injury and illness compared to those working in construction, manufacturing, or transportation sectors.
That is according to the US Bureau of Labour Statistics on non-fatal injuries and illness by industry. As shown in the 2021 statistics below, hospitals and nursing homes have significantly higher injury rates than most industries. This trend has been consistent over the past few years, with a spike in incident rate for healthcare workers in 2020 due to Covid-19.
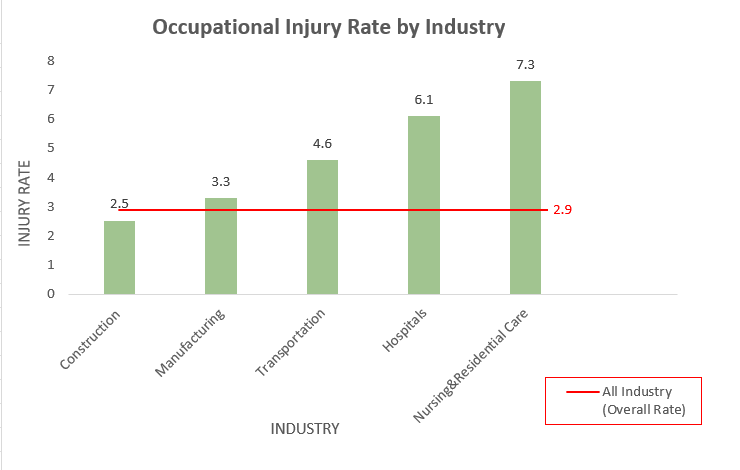
Note: The incident rates represent the number of injuries and illness per 100 full-time workers per year.
Source: US Bureau of Labour Statistics
Key Statistics
While the statistics in other regions or countries (if available) may differ from the US, occupational hazards in the healthcare sector have been highlighted in various studies, as listed below:
- Globally, 62% of healthcare workers report experiencing various forms of violence at the workplace. Verbal abuse (58%) is the most common form of non-physical violence, followed by threats (33%) and sexual harassment (12%).
- During the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic, 23% of front-line healthcare workers worldwide suffered depression and anxiety and 39% suffered insomnia. Furthermore, medical professions are at higher risk of suicide in all parts of the world.
- Between 44% and 83% of nurses in clinical settings in Africa have chronic lower back pain, compared to 18% among office workers.
- Needle stick injuries contributed to 39% of hepatitis C and 37% of hepatitis B infections.
Source: WHO, Occupational Health: Health Workers
What do these statistics tell us about healthcare worker health and safety? How is staff health and safety connected to patient safety? What urgent actions can hospital management take?
Occupational Hazards in Healthcare Sector
Healthcare is a high-risk, high-demand, high-stress industry in constant change, one with unique health and safety challenges. Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, technicians, and support staff, face numerous hazards and potential sources of injury and illness in the workplace. Unsafe patient handling accounts for a significant portion all healthcare injuries reported in hospitals. Healthcare workers also face some of the greatest risk for workplace violence and harassment by patients. Another major source of occupational hazard is stress, burnout, and fatigue.
The following are some of the most common occupational hazards and injuries in hospitals:
- Unsafe patient handling
- Occupational stress, burnout, and fatigue
- Violence and harassment
- Occupational infections
- Occupational injuries (eg. slips, trips, and falls)
- Exposure to hazardous chemicals
- Exposure to radiation
Prioritizing Healthcare Worker Safety
In healthcare, patient safety is the top priority. This has long been the traditional focus of healthcare providers and one that has been embedded through the education system and the medical profession. Healthcare organizations’ strategic focus is patient safety. Workplace health and safety is not widely understood or addressed as a strategic priority in hospitals.
For most hospitals, investments in systems, processes, controls, and technologies are mostly aimed at improving patient safety. Resources are primarily allocated to meet the needs of patients, often leaving the health, safety, and well-being of staff under-addressed.
There is an urgent need for a shift in strategic focus to give equal priority to both staff and patient safety. The COVID-19 pandemic has made abundantly clear how dependent patient safety is on healthcare worker safety. An integrated and systemic management approach that includes ensuring staff safety and well-being is crucial to preventing systemic failures. Only when healthcare workers are safe can they keep patients safe and provide health systems with stability and resilience.
Creating a Culture of Safety in the Workplace
Recognizing healthcare worker safety is a prerequisite for patient safety, hospitals and other healthcare providers should prioritize staff health and safety and create a culture that promotes open communication, reporting of safety concerns, and the implementation of preventive measures to ensure a safe and healthy work environment for all employees. The following are key strategic actions healthcare organizations can take:
- Incorporate healthcare worker health and safety into the overall patient safety policies and strategies
There can be no patient safety without healthcare worker safety, as both are inseparably connected in practice. Health and safety risks to healthcare workers can lead to risks for patients, patient harm, and adverse patient outcome. Healthcare providers should give equal priority to healthcare worker safety and take a holistic approach in managing healthcare worker safety, patient safety, quality improvement and infection prevention and control programmes. This strategic change can contribute to safer and quality care, reducing costs due to healthcare worker attrition and suboptimal productivity. Hospital management needs to:
- Incorporate workplace safety and health (WSH) policies and guidelines into the organizational policies and guidelines on safety.
- Promote awareness on healthcare worker health and safety.
- Provide training programs on health and safety skills pertaining to staff safety and patient safety to all healthcare workers.
- Include WSH incidents in patient safety incident reporting system.
- Develop performance indicators on healthcare worker safety, along with patent safety and quality of care indicators.
- Protect healthcare workers from violence in the workplace
Violence in the workplace occurs in the form of abuse, harassment, and discrimination. Healthcare workers across the world face physical and psychological violence in their daily work. These threats directly affect morale and hamper retention of healthcare workers and can lead to reductions in patient safety and quality of care. Within this context, hospital management needs to:
- Implement policies and guidelines to protect healthcare workers against violence.
- Promote a culture of zero tolerance of violence against healthcare workers.
- Establish relevant implementation mechanisms, such as helplines and anonymous reporting of incidents.
- Render support for any healthcare workers facing violence.
- Improve mental health and physical well-being of healthcare workers
Many healthcare workers work in high-demand, high-risk and high-stress work settings for long hours. This makes them susceptible to mental health and psychological well-being issues. The link between negative working conditions and employee stress is well researched. Work stress and burnout are also associated with quality of patient care and patient safety. Healthcare workers should be given access to psychological support and able to report safety concerns without fear of retaliation. Within this context, there is a need to:
- Establish policies to ensure appropriate working hours and rest breaks.
- Maintain appropriate staffing levels.
- Minimize the administrative burden of healthcare workers.
- Promote a blame-free and just working culture through open communication.
- Provide access to mental wellbeing and social support services to healthcare workers.
- Protect healthcare workers from physical and biological hazards.
Healthcare workers in hospitals face multiple physical, biological, and ergonomic hazards including exposure to infections, sharps, falls, radiation, chemicals or musculoskeletal disorders due to poor ergonomics in handling patients and lifting heavy equipment. Management can take the following actions:
- Ensure the implementation of minimum patient safety, infection prevention and control, and occupational safety standards in all healthcare facilities across the health system;
- Always ensure the availability of personal protective equipment (PPE). Undertake adequate training on the appropriate use of PPE and safety precautions;
- Ensure vaccination of all at-risk healthcare workers against vaccine preventable infections. In the event of virus outbreak, giving healthcare workers priority access to the available vaccines;
- Provide adequate resources and training to prevent healthcare workers from injury and harmful exposure to chemicals and radiation;
- Provide functioning and ergonomically designed equipment and workstations to minimize musculoskeletal injuries and falls.
Source: Adopted from WHO Charter on Health Worker Safety: A Priority for Patient Safety
Benefits of Investing in Healthcare Worker Safety
Investing in healthcare worker health and safety has far-reaching benefits for healthcare organizations, employees, and patients alike. It creates a safer and more efficient and resilient healthcare system that ultimately contributes to better health outcomes, more sustainable healthcare workforce and operational resilience.
Other industries, especially safety-critical industries, have long recognized the connection between a safe workforce, excellent customer care and high performance. These sectors have strategic oversights on workplace safety and health, and integrate these policies into their core business, risk management and corporate governance.
A systematic focus on healthcare worker safety and wellbeing has been reported to have the following follow-on effects:
- Increased quality of patient care and service
- Decreased absenteeism and overtime
- Reduced lost time (caused by injuries or sickness)
- Reduced need for agency staff (lower costs)
- Higher staff retention
- Improved communication and teamwork
- Higher work satisfaction and productivity
- A healthier, stable workforce
Source: Adopted from Sikorski – Connecting Worker Safety to Patient Safety: A New Imperative for Healthcare Leader
Conclusion
Healthcare worker safety and patient safety are two critical aspects of healthcare that are closely interconnected and mutually dependent. Ensuring the safety of both staff and patients is essential for delivering high-quality healthcare services. Both should be given equal priority. Investing in healthcare worker safety will benefit healthcare organizations, employees, and patients. It creates a safer, more efficient, and resilient healthcare system.
QUASR supports healthcare worker safety by enabling quick and easy reporting of workplace incidents and near misses in all healthcare settings.






