In an era defined by uncertainty and rapid transformation, Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) management serves as a strategic framework for navigating complexities and achieving organizational goals. By integrating governance, risk mitigation, and compliance efforts, businesses can strengthen resilience, enhance decision-making, and secure long-term success.
What Is GRC Management?
GRC management refers to the structured coordination of governance policies, risk management practices, and compliance processes within an organization. By aligning these critical functions, organizations ensure that decisions are made with a holistic understanding of risks, opportunities, and regulatory obligations.
The ultimate goal of GRC is to foster a culture of accountability, enabling businesses to adapt to challenges while safeguarding their reputation and resources.

The Role of Technology in GRC
Modern GRC management relies heavily on technology. Advanced tools provide real-time insights, streamline processes, and facilitate collaboration across departments. Key technological advancements include:
• Automation: Reducing manual effort and human error in compliance tracking and risk assessments.
• Data Analytics: Offering actionable insights through predictive analytics and scenario modeling.
• Integrated Platforms: Unifying governance, risk, and compliance data for a cohesive approach.
Investing in the right technology empowers organizations to respond swiftly to emerging risks and regulatory changes.

Key Principles of GRC Management
1. Integration: Break silos by uniting governance, risk, and compliance functions.
2. Proactive Risk Management: Identify and mitigate risks before they escalate.
3. Continuous Improvement: Adapt frameworks to address evolving challenges.
4. Collaboration: Foster cross-functional teamwork to enhance accountability.
5. Transparency: Promote openness in decision-making and reporting processes.
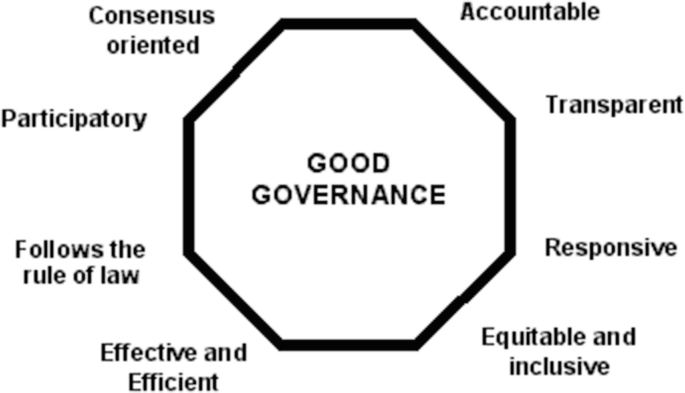
Governance: The Backbone of Organizational Integrity
Governance establishes the foundation for ethical behavior and strategic alignment. Its key elements include:
• Leadership Oversight: Defining roles and responsibilities for decision-making.
• Policy Frameworks: Establishing guidelines for consistent operations.
• Performance Monitoring: Tracking key metrics to ensure organizational goals are met.
• Stakeholder Engagement: Aligning business objectives with stakeholder expectations.
Effective governance builds trust and sets the stage for sustainable growth.
Risk Management: Safeguarding the Organization’s Future
Risk management is about identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats. Key aspects include:
• Risk Identification: Mapping out vulnerabilities across operations.
• Risk Assessment: Prioritizing risks based on impact and likelihood.
• Mitigation Strategies: Implementing measures to reduce or transfer risk.
• Continuous Monitoring: Keeping track of risk indicators for timely interventions.
A proactive approach to risk ensures business continuity and resilience.

Compliance: Ensuring Adherence to Laws and Regulations
Compliance ensures that organizations operate within the boundaries of applicable laws and standards. This involves:
• Regulatory Awareness: Staying informed about changing legal landscapes.
• Policy Implementation: Translating regulations into actionable business practices.
• Auditing and Reporting: Demonstrating compliance to regulators and stakeholders.
• Training Programs: Building awareness and adherence among employees.
Maintaining compliance mitigates legal risks and strengthens organizational credibility.
How Does GRC Improve Decision-Making?
Effective GRC practices elevate decision-making by providing a structured, strategic approach.
1. Informed Decisions: Access to consolidated data enables a clearer understanding of risks and opportunities.
2. Balancing Short-Term and Long-Term Goals: Aligning immediate objectives with sustainable outcomes.
3. Promoting Accountability and Transparency: Ensuring decisions are ethical and accountable to stakeholders.
4. Strategic Advantage: Leveraging insights to turn decision-making into a competitive edge.
Organizations that embrace GRC as a decision-making tool are better positioned to seize opportunities and mitigate challenges. Tasks, Dashboards and Reports are key for decision-making.

How Does GRC Benefit Businesses?
GRC frameworks provide numerous benefits, including:
• Enhanced Risk Awareness: Proactively identifying and managing risks.
• Streamlined Operations: Reducing redundancies and optimizing processes.
• Reputation Management: Building trust among customers, investors, and regulators.
• Cost Savings: Avoiding penalties and reducing inefficiencies.
• Competitive Advantage: Strengthening resilience and adaptability in a dynamic market.

How to Establish a GRC Model: A Practical Guide
1. Define Objectives: Align GRC initiatives with organizational goals.
2. Conduct a Gap Analysis: Identify weaknesses in current governance, risk, and compliance processes.
3. Implement Technology: Choose tools that unify and automate GRC activities.
4. Develop Policies and Procedures: Establish clear guidelines for operations.
5. Train Employees: Build awareness and accountability across teams.
6. Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review and refine GRC strategies to ensure continued relevance.

Next Steps...
Are you ready to transform your organization’s approach to Governance, Risk, and Compliance? Take the first step toward a resilient and sustainable future. Contact us today to learn how our comprehensive GRC solutions can empower your business!






